Key Concepts:

- Frequency (Hz)
- Wavelength (m)
- Amplitude (pressure)
- Speed of sound (m/s)
- Resonance
- Interference
- Diffraction
Applications:
- Music and audio engineering
- Architectural design (echo reduction)
- Medical imaging (ultrasound)
- Non-destructive testing
- Noise reduction

Thermodynamics:
Study of heat, temperature, and energy transfer
Key Concepts:
- Temperature (K)
- Heat transfer (conduction, convection, radiation)
- Energy conversion (work, heat)
- Laws of thermodynamics (Zeroth, First, Second, Third)
- Entropy
- Thermodynamic systems (open, closed, isolated)
Applications:
- Power generation (engines, turbines)
- Refrigeration and air conditioning
- Materials science (phase transitions)
- Chemical engineering (reaction kinetics)
- Aerospace engineering (heat shields)
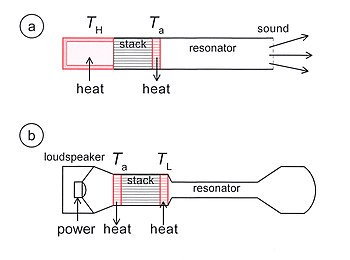
Relationship between Acoustics and Thermodynamics:
- Sound waves can generate heat through friction and viscosity.
- Temperature affects sound wave propagation (speed and frequency).
- Thermodynamic processes can produce sound (e.g., boiling water).
Equations and Formulas:

Acoustics:
- Wave equation: ∂²u/∂t² = c²∇²u
- Frequency-wavelength relation: f = c/λ
Thermodynamics:
- Ideal gas law: PV = nRT
- Heat transfer equation: Q = mcΔT








